Definition Of Poisson Distribution
Poisson Distribution is one of the types of Discrete Distribution. A Random Variable X is said to follow Poisson Distribution with parameter λ, if its probability mass function is given by:This is the Poisson Distribution formula.
where λ is the average occurrence per unit time or space over a certain period to time or space.
where λ = np
Jump to Probability and Queuing Theory Index Page
Applications of Poisson Distribution:
Here are some applications of Poisson Distribution:- the arrival of customers at a service station.
- The number of telephone calls to a mail order service.
- Typographical errors in manuscripts.
- The number of defects in a fabric.
- The number of machine breakdown in a day.
- The number of accidents in a highway.
It is used for counting the number of events which occurs over time or space.
What are the conditions to use Poisson Distribution?
- The number of the trial (n) is large.
- The probability of success in a trial is small. i.e p is small
Mean of Poisson Distribution:
The mean of the Binomial Distribution is denoted by μ or E(X)
E(X) = λ
The variance of Binomial Distribution:
The variance of the Binomial Distribution is denoted by σ2 or V(X).
V(X) = λ
Use of New Parameter in Poisson Distribution:
α = λ.T
Here α is the new parameter and T is the Time period. α gives the average occurrence per unit over a time period T.
Poisson Distribution Examples:
Solved Problem 1: It is known that 5% of the books bound at a certain bindery have defective bindings. Find the probability that 2 of the 100 books bound by this bindery will have defective bindings using Poisson Distribution?
= Solution:
here given,
number of trials (n) = 100
Probability of success (p) = 5% = 0.05
so, q = 1 - p = 0.95
Let X be the random variable for defective bindings.
We know that,
λ = np = 100*0.05 = 5
we have,
P(X = 2) = (e-5.λ2) / 2! = 0.084
Solved Problem 2: The arrival of a truck at a receiving dock is a Poisson Process with a mean average rate of 2 per hour.
a. Find the probability that exactly 5 trucks arrive in a two hour time period?
b. Find the probability that 8 or more trucks arrive in two hour period?
= Solution:
here given,
average arrival rate = λ = 2 per hour
arrival rate in 2 hour time period (T = 2) is
α = λ.T = 2*2 = 4 trucks per 2 hour.
a. the probability that exactly 5 trucks arrive in a two hour time period is:
P(X = 5) = (e-α.αx) / x!
= (e-4.45) / 5!
= 0.15
= (e-4.45) / 5!
= 0.15
b. the probability that 8 or more trucks arrive in two hour period is:
P(X ≥ 8) = 1 - P(X < 8)
= 1 -[P(X=0)+P(X=1)+P(X=2)+P(X=3)+P(X=4)+P(X=5)+P(X=6)+P(X=7)]
= 1 - [(e-4.40) / 0! + (e-4.41) / 1! + (e-4.42) / 2! + (e-4.43) / 3! + (e-4.44) / 4! + (e-4.45) / 5! + (e-4.46) / 6! + (e-4.47) / 7!]
= 1 -[P(X=0)+P(X=1)+P(X=2)+P(X=3)+P(X=4)+P(X=5)+P(X=6)+P(X=7)]
= 1 - [(e-4.40) / 0! + (e-4.41) / 1! + (e-4.42) / 2! + (e-4.43) / 3! + (e-4.44) / 4! + (e-4.45) / 5! + (e-4.46) / 6! + (e-4.47) / 7!]
Poisson Distribution with Formulas and Examples
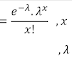 Reviewed by Sandesh Shrestha
on
04 July
Rating:
Reviewed by Sandesh Shrestha
on
04 July
Rating:
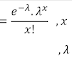 Reviewed by Sandesh Shrestha
on
04 July
Rating:
Reviewed by Sandesh Shrestha
on
04 July
Rating:







No comments: